reaction injection moulding
Release date:2021-06-04
Reaction injection moulding (reaction injection moulding, abbreviated as RIM), an industrial molding process. In the molding process, there is a chemical reaction injection molding method. The raw material used in this method is not a polymer, but two or more liquid monomers or prepolymers are added to the mixing head in a certain proportion. Mix uniformly under pressure, immediately inject into a closed mold, polymerize and solidify in the mold, and shape into a product. Because the raw material used is liquid, the cavity can be quickly filled with a small pressure, so the clamping force and the cost of the mold are reduced, and it is especially suitable for the production of large-area parts.
RIM was originally only used for polyurethane materials. With the advancement of process technology, RIM can also be applied to the processing of a variety of materials (such as epoxy, nylon, polyurea, polycyclopentadiene, etc.). The RIM process for rubber and metal molding is a hot spot of current research
Reaction injection molding was developed in the late 1970s. The United States adopts the reaction injection molding method to make polyurethane semi-rigid plastic automobile bumpers, fenders, dashboards, etc. with isocyanate and polyether. This method has the advantages of low equipment investment and operating cost, beautiful appearance, good impact resistance, and great design flexibility. It developed rapidly in the 1980s. Reaction injection molding can also produce foam with a rigid surface layer of polyurethane structure. In order to further improve the rigidity and strength of the product, it is called enhanced reaction injection molding when various reinforcing materials are mixed into the raw materials. The product can be used as the outer panel of the automobile body and the engine cover. The newly developed varieties include epoxy resin, dicyclopentadiene polymer, silicone resin and interpenetrating polymer network.
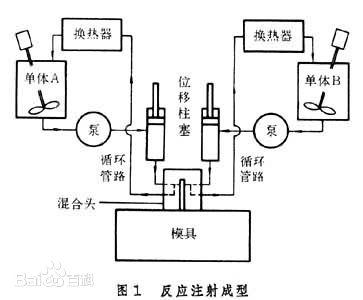
Reaction injection molding requires that the components react quickly once they are mixed, and the material can be cured to the extent that it can be demolded. Therefore, special raw materials and formulas must be used, and sometimes products need heat treatment to improve their performance. The key to the molding equipment is the structural design of the mixing head (Figure 2 [Mixing head structure]), accurate metering and delivery of each component. In addition, the temperature control of raw material storage tanks and molds is also very important.

